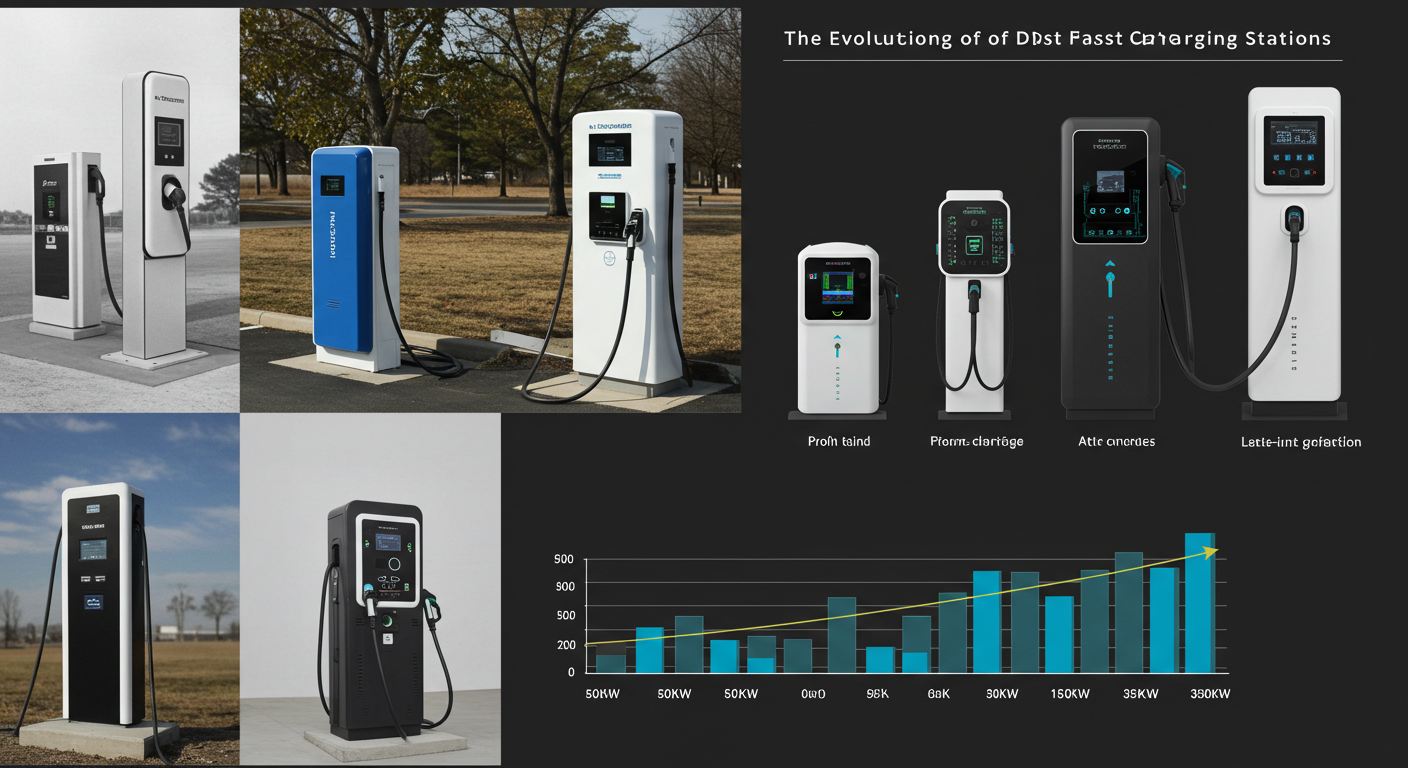
Introduction
As electric vehicles (EVs) become increasingly prevalent on our roads, the infrastructure supporting them is also evolving. DC fast charging stations, which were once limited to just one or two plugs, are now expanding in size and capacity to meet the growing demand. This article explores the transformation and future of DC fast charging stations.
The Shift in DC Fast Charging Infrastructure
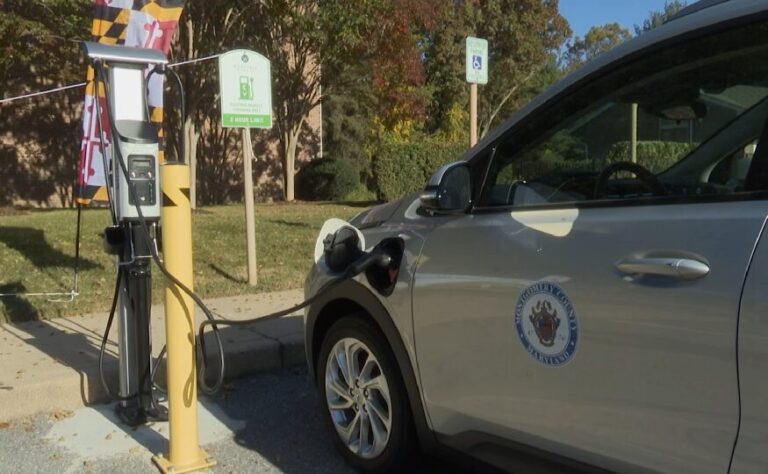
Traditionally, DC fast chargers were designed to accommodate a limited number of vehicles simultaneously, which often led to long wait times for drivers. However, with the rising adoption of electric vehicles, the need for more robust charging solutions has prompted a significant shift in infrastructure development. As manufacturers and service providers recognize the growing need for efficiency, many are now deploying larger charging stations equipped with multiple plugs.
Benefits of Larger Fast Charging Stations
- Increased Availability: By providing more charging ports, these stations can reduce wait times, making it more convenient for EV drivers.
- Enhanced Power Output: Larger stations often come with higher power outputs, allowing for faster charging times.
- Scalability: As the EV market continues to grow, larger charging stations can be expanded to accommodate future demand.
- Integration with Renewable Energy: Many new fast charging stations are being designed to integrate with renewable energy sources, further enhancing their sustainability.
Real-World Examples of Expansion
Several companies have taken the lead in this charging revolution. For instance, major players in the electric vehicle charging market are installing stations with capabilities to charge multiple vehicles at once. These advancements are not only beneficial for consumers but also for businesses looking to attract EV drivers.
The Future of DC Fast Charging Stations
Looking ahead, the trend towards larger DC fast charging stations is expected to continue as electric vehicles become more mainstream. Industry experts predict that new technologies will emerge, further enhancing charging speeds and efficiencies. In addition, as battery technology improves, charging stations will need to adapt to meet the evolving needs of consumers.
Conclusion
The growth of DC fast charging stations signifies a critical step in the transition to electric mobility. As more drivers make the switch to EVs, the necessity for expanded charging infrastructure will only increase. The shift towards larger, more capable charging stations not only improves the user experience but also supports the broader goals of sustainability and renewable energy integration.